Thanks to advances in technology and evolving consumer demand, the healthcare industry is experiencing a massive shift in delivery of care. Today’s patients want greater visibility and control of their own health instead of having information and decisions siloed with healthcare providers. At the same time, a rise in chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, diabetes, and other illnesses — as well as a growing aging population throughout the world — means that the industry must innovate to scale quickly and effectively.

One way to reduce the pressures on traditional care settings is to empower patients to monitor various health parameters and manage elements of their own care through connected health and wearable medical devices. Consumers already expect this of their devices; consider how heart rate monitors are integrated into popular devices like smartwatches. The opportunity for manufacturers of wearable medical devices is enormous; according to Deloitte’s 2023 Global Health Care Outlook report, “the global market for remote monitoring devices is expected to grow to more than $101 billion in 2028.” The same report also states that “by 2024… almost 440 million consumer health and wellness wearable devices will ship worldwide.”
Another report by Market.us looks even further out to forecast that the wearable diagnostic and monitoring devices market will reach $165 billion by 2032, commanding the biggest share of the broader wearables market that includes fitness and wellness trackers.

To successfully capture these opportunities while delivering safe, reliable, and effective patient care, MedTech companies must prioritize three key areas when bringing wearable medical devices to market:
- Product design and engineering
- Advanced manufacturing capabilities
- Strategic regionalization
Together, these elements will empower companies to get their innovations to market faster and scale amid explosive demand.
Designing wearable medical devices faster and more effectively
To compete in the wearable medical device market, companies must prioritize user-centered design and deep engineering expertise to specify, conceptualize, develop, test, and sustain their products.
Design for Manufacturing is a key step early in product design, as it helps companies identify opportunities and unexpected challenges in the manufacturing process. This allows MedTech companies to maximize investments, reduce time-to-market, and eliminate the risk of discovering design issues in their wearable medical devices during full-scale production. For example, by considering the durability and availability of materials used in wearable medical devices, companies can future-proof their designs, minimizing technical obsolescence and other future risks.
As sustainability continues to grow in importance across every industry, Design for Manufacturing also enables MedTech companies to define the sustainability requirements during product design, such as choosing biodegradable materials or ensuring that a product can be recycled or refurbished effectively and responsibly. For example, at Flex we have worked with healthcare clients to identify how a product design could be altered for improved sustainability outcomes.
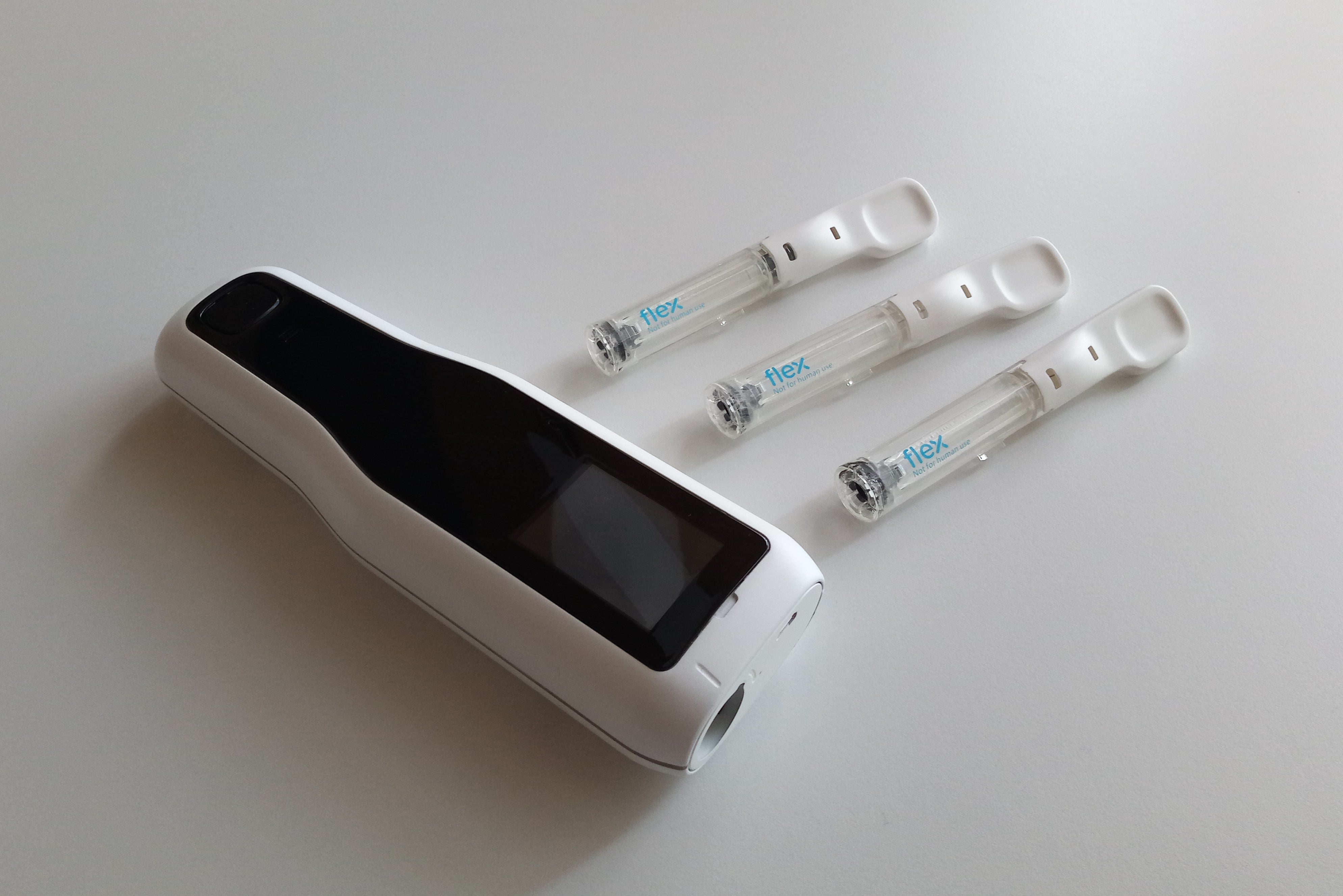

In one case, we developed a smart autoinjector design reference platform that utilizes eco-friendly materials, as well as minimized welding and gluing of internal parts during the assembly and manufacturing process. This resulted in sustainability benefits later in the product lifecycle, including streamlined unit breakdown and components recycling that reduced the volume of waste.
As wearable medical devices become more popular, blurring the line between consumer and medical devices, other challenges arise. A paper published by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security states that “while wearable healthcare devices offer consumers the ability to be an active participant in managing their health… devices may include vulnerabilities that allow the device to be compromised and expose personal data.”
To that end, MedTech companies must continue to learn from both within their own industry and from other highly regulated industries, adopting best practices to confidently design and architect products with the utmost level of security. At Flex, we are committed to establishing secure connectivity standards across multiple industries. As a member of the Project Centauri partner ecosystem, we continue to refine and apply these standards to healthcare and connected medical device applications to deliver quality, security, and seamless connectivity.
Advanced manufacturing to boost medical device production
Competing in today’s fast-paced global landscape requires access to a full suite of advanced manufacturing capabilities and Industry 4.0 technologies that enable MedTech companies to scale faster and more reliably. Rather than designing and manufacturing all products in-house, many companies are increasingly turning to global, diversified manufacturers like Flex to accelerate time-to-market, better manage risk, provide greater scalability, and improve market responsiveness.
Given the importance of precision, quality, and long-term reliability in medical devices, MedTech companies must find ways to scale and become more efficient while still maintaining stringent standards and requirements. Technologies such as automation can reduce the pressures of labor shortages and supply chain constraints when producing wearable medical devices.

One example of how we’ve improved manufacturing processes for our customers is the way we leveraged digital twin technology to accelerate the delivery of a diabetes product. With the power of a digital twin, we reiterated the product model hundreds of thousands of times, ran “what if” scenarios, and tested dozens of variables. As a result, something that would have taken three months or longer was reduced to only three weeks.
Regionalization and global reach to get products when and where they are needed
In today’s uncertain world, many brands have adapted to a regionalized model, wherein companies re-shore part of their operations to be closer to the markets they serve. This strategy mitigates risk, ensures business continuity, and speeds time-to-market. In a 2022 McKinsey & Company survey of 113 supply chain leaders worldwide, 44% of respondents, up from 25% percent the previous year, stated that they were developing regionalized supply networks.
Regionalization enables MedTech companies to source components and build products in-region, or to rapidly shift production to other worldwide locations as demand or regulations change. A regionalization strategy comes with more benefits than just risk mitigation — it can also speed time-to-market and help companies meet increasing sustainability requirements. Put simply, moving closer to the markets they serve enables companies to be more resilient and competitive while also protecting the environment.
Another recent McKinsey & Company study identifies medical devices as one of the top ten industries with “strong regionalization feasibility,” stating that for companies falling in this category, “regionalization offers agility and flexibility in an unpredictable global trading landscape.”
The future of healthcare is wearable
To meet the growing demand for wearable medical devices, MedTech companies must adopt a strategy that provides a competitive edge at every step of the process — from design and engineering to full-scale production, to delivering products to the end user. Beyond the three priority areas discussed above, wearable medical device manufacturers can also boost competitiveness by tapping into deep domain knowledge and an extensive toolkit of technological advancements that includes sensor chips, miniaturization, and battery life, as well as connectivity with high-speed data transmission, artificial intelligence, and security.
Ultimately, the wearable medical device market is poised to make an enormous impact on the healthcare industry, relieving cost pressures and streamlining care as the site of care shifts downstream from hospitals to patient homes. Though the scope of the challenge is vast, so too is the opportunity.
As an industry, we must rise to meet it.